Published Feb 11, 2025
How to use a Lookup Cache for large dataset mappings
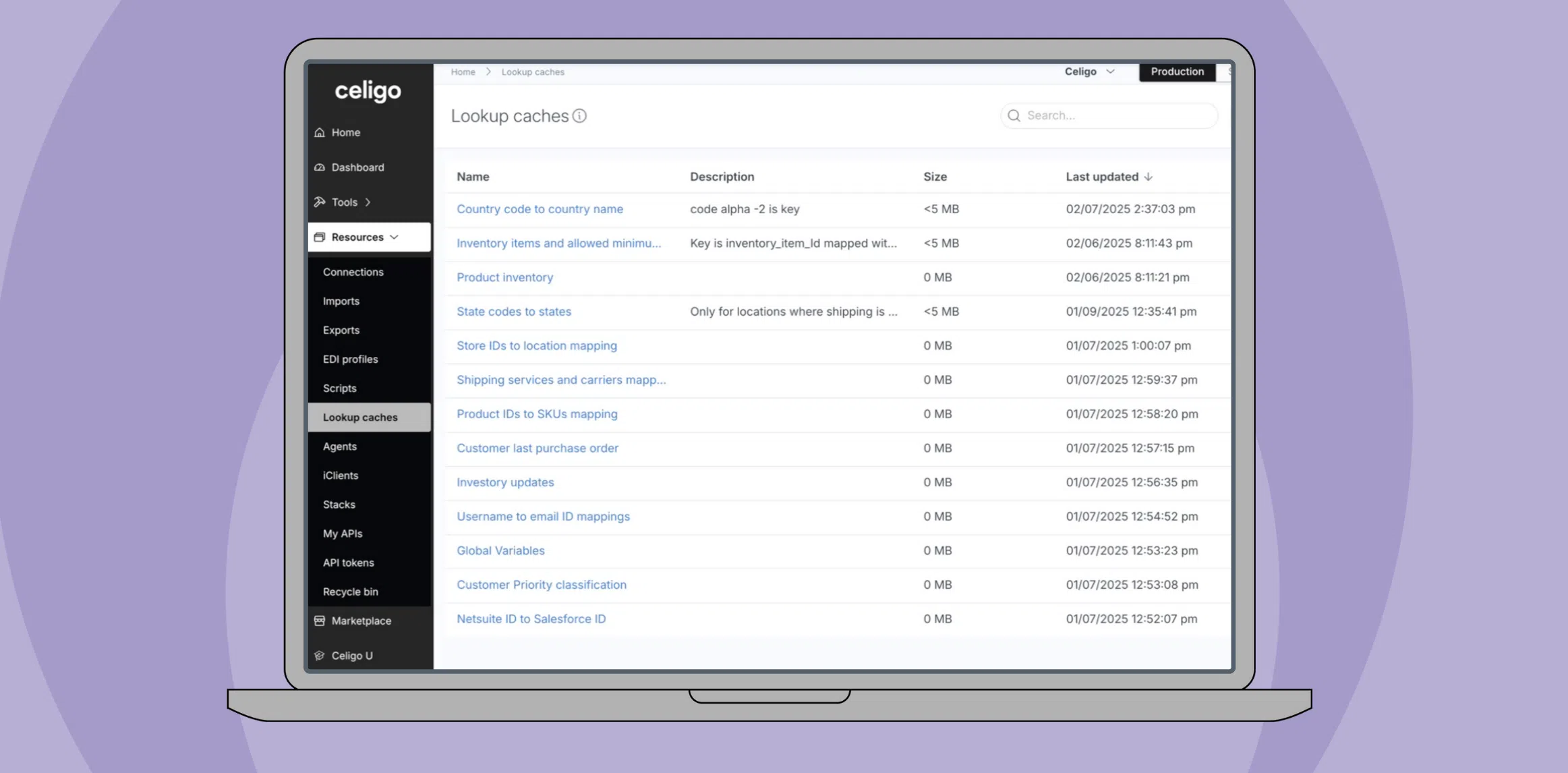
Lookup Caches act as a central repository for frequently used data, stored in a key-value format. This allows you to store, find, and reuse data across flows without relying on repeated API calls or external database queries.
→ Learn more about the Lookup Cache.
Lookup Cache demo
Lookup Cache overview
Why use Lookup Caches in your flows?
- Faster data lookups: Reduces dependencies on external systems, improving flow efficiency.
- Scalable mappings: Handles large datasets better than static or dynamic lookups.
- Reusable and flexible: Acts as a lookup table, environment-specific variable store, or centralized reference data repository.
- Easier maintenance: Data can be loaded via CSV files or updated dynamically using Integrator.io APIs.
Many integrations require mapping and transforming data between different formats.
For example:
- One system may store country and state data as two-letter codes, while another requires full names.
- Maintaining these mappings manually is time-consuming, error-prone, and difficult to scale, especially with large datasets.
A Lookup Cache solves these challenges by storing transformation rules centrally, ensuring faster, more reliable, and scalable mappings.
Use case: Mapping country codes to full names
Imagine syncing customer data from Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central to Shopify:
- Business Central stores country and state information as two-letter codes.
- Shopify requires full country and state names.
Instead of relying on:
- Static lookups, which are difficult to maintain
- External API calls, which slow down processing
You can use Lookup Cache to transform values within your integration instantly.
How to use Lookup Cache for mappings
Step 1: Configure the mapper
- Open Mapper 2.0 in your flow.
- Select the destination field (e.g., “Country” in Shopify).
- Select the source field (e.g., “Country Letter Code” from Business Central).
Step 2: Create a Lookup Cache
- Change the field mapping type to Lookup and select Lookup Cache.
- If an existing Lookup Cache is available, select it. Otherwise, create a new one.
- Upload a CSV file containing mappings for two-letter country codes and full names.
- Choose the key column (e.g., “Alpha-2” for two-letter country codes).
- Choose the value column (e.g., “Full Country Name”).
- Configure whether the data should persist when cloning or moving the flow.
Step 3: Apply the Lookup Cache in the mapper
- Select Lookup Cache as the mapping source.
- Set the value field to return the full country name.
- Save and apply the changes.
Step 4: Run the flow and verify the data
- Execute the flow to sync customer records.
- In Shopify, confirm that country names now appear in full instead of two-letter codes.
Benefits of using the Lookup Cache
Lookup Cache provides a scalable, efficient solution for transforming large datasets in integrations. Storing and applying mappings improves accuracy, reduces reliance on external systems, and accelerates data processing.
- Faster processing: Avoids repeated API calls for lookups.
- Scalability: Handles large datasets without performance issues.
- Easy maintenance: Update lookup values centrally without modifying each flow.
- Greater accuracy: Eliminates errors from manual mappings.

